HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages.

What is HTML?
- HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language.
- It is used to create the structure of the webpage.
- HTML is a markup language, not a programming language.
- HTML elements tell the browser how to display the content
- HTML describes the structure of a Web page
HTML Page Structure
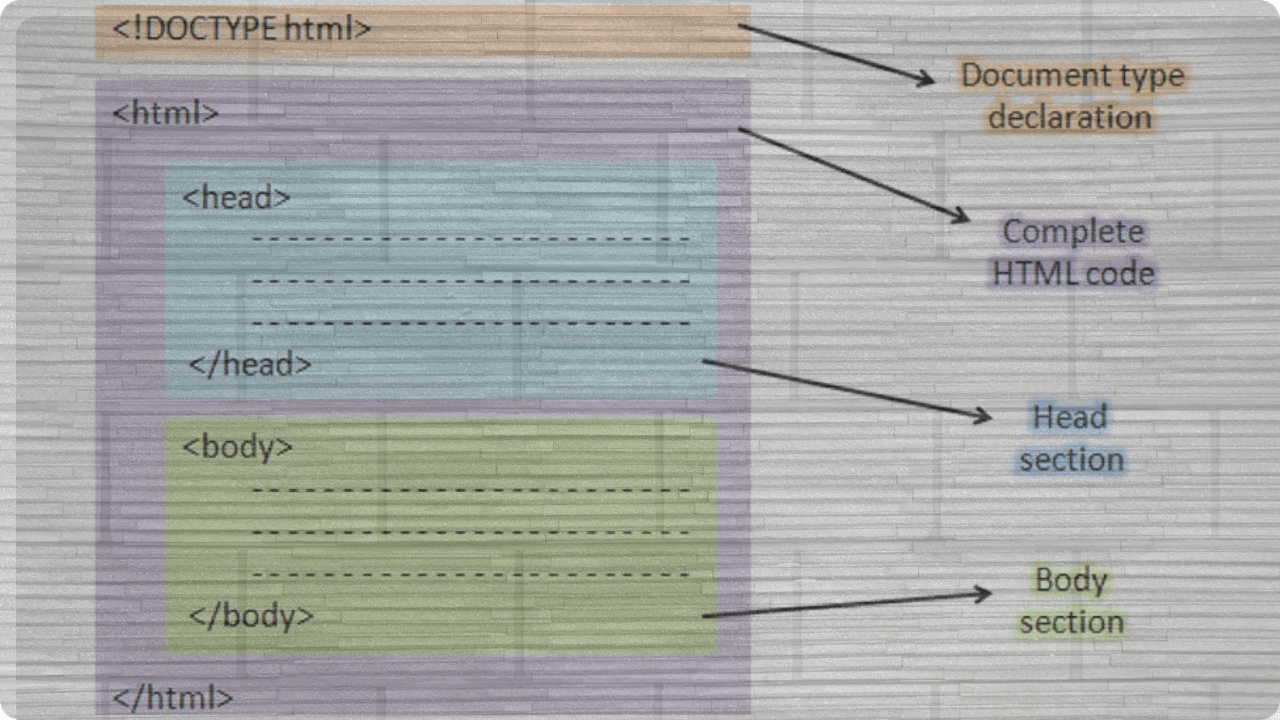
Basic Structure of an HTML Document
An HTML document typically consists of the following elements:
- DOCTYPE Declaration: Tells the browser which version of HTML is being used. For HTML5, it’s written as <!DOCTYPE html>.
- <html> Tag: Contains the entire HTML document.
- <head> Tag: Holds meta-information about the page, like the title and links to CSS files.
- <body> Tag: Contains the main content of the page.
Here’s a simple example of an HTML document:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>My First HTML Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Welcome to My First HTML Page</p>
<p>This is a paragraph of text.</p>
<a href="https://www.example.com" rel="nofollow noopener" target="_blank">Visit Example.com</a>
</body>
</html>
HTML History
Since the early days of the World Wide Web, there have been many versions of HTML:
1. Early Beginnings (1989-1991):
– 1989: Tim Berners-Lee, a scientist at CERN, had an idea to create a system to share documents easily.
– 1990: Berners-Lee created the first version of HTML. It had 18 tags (codes to format and link documents).
– 1991: The first webpage was made. It explained how to create and use webpages.
2. HTML 2.0 (1995):
– The first official version of HTML. It included basic tags and was standardized by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).
3. HTML 3.2 (1997):
– Improved by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), a group that helps develop web standards.
– Introduced new tags for tables, applets (small programs), and text styling.
4. HTML 4.01 (1999):
– A more robust version with better support for complex webpages.
– Included improvements for accessibility (making websites usable for people with disabilities).
5. XHTML (2000):
– A stricter version of HTML, designed to work better with other languages like XML.
– Emphasized cleaner, more precise code.
6. HTML5 (2014):
– A major update with new features for modern web needs.
– Added support for video and audio playback, interactive elements, and better performance on mobile devices.
– Focused on creating a more dynamic and interactive web experience.